Choice of location: cornerstone for the success of European companies in China
Site selection is an important factor for European companies in greenfield investment projects in China. Aspects such as operating costs, transportation, preferential policies, political risks, labor market conditions, etc. will have a direct impact on the operation and competitiveness of companies in the future, in this respect, a wise decision for the future direction is of key importance.
Not only the subsequent change of the company address can cause financial costs, but also the move to a new location means a considerable logistical and organizational effort.
Essential factors for the choice of location from the point of view of CLEVANA CONSULTING
For European companies investing in China, it is usually about building sales and technical teams, setting up production facilities, and building factories in China. We believe that not only the company’s development strategy and the current industry situation in the different regions of China are relevant, but also the economic, political, and social characteristics in each region and city.
We usually analyze the following factors in advance:

Manpower and corresponding costs
Workers play a central role in the operation of a company. They are the driving force for continuous growth, healthy development, and a future expansion policy.
For talent-oriented industries and companies in the areas of technological research and development, precision mechanical manufacturing, or distribution, it is necessary to include the local and regional labor market situation and labor costs in the site selection process.
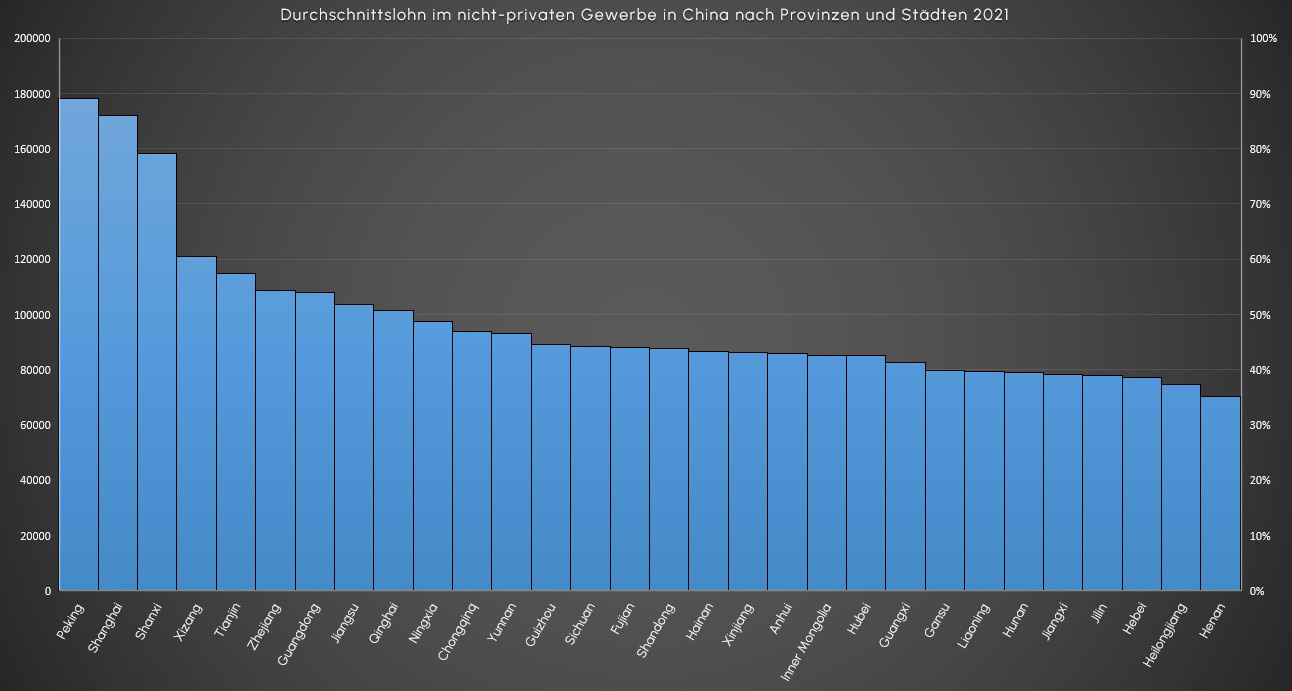 Data source: China Statistical Yearbook-2021 (unit: RMB, yuan)
Data source: China Statistical Yearbook-2021 (unit: RMB, yuan)
But it is not only labor costs that affect the choice of location. The qualifications of the local workforce also play an important role. Metropolitan areas such as Beijing and Shanghai, which have a high density of universities and colleges, guarantee a far higher number of qualified employees than more rural regions.

Regional industrial environment
China is an extremely large country with a total area of 9.6 million square kilometers. Large differences exist here between the regions in the north and south, east and west. Each region has its own economic cluster characteristics for different sectors and industries and has different cluster formation mechanisms, such as resource-driven, trade-driven, science and technology resource-derived, and industry transfer-driven clusters.
Multiple resources converge in different industry clusters, such as technological research and development, supply chains, markets, talent, transportation, and public facilities in upstream and downstream industry chains.
Example: Starbucks
In 2020, Starbucks invested nearly 1.1 billion yuan in the Kunshan Industrial Park in Jiangsu Province for its China Coffee Innovation Project. The choice of location was influenced on the one hand by the fact that Kunshan is less than an hour’s drive from Shanghai and Jiangsu Province, grew into one of the largest industrial parks in China, and attracted a large number of German companies. On the other hand, the location in Kunshan lent itself in terms of its coffee industrial chain. The industrial park had previously carried out a single coffee bean roasting project. Then Starbucks’ OEM was brought in and they developed a business plan that included warehousing and delivery to roasting and brand sales.
Wei Chuan Foods Corporation, for example, helped Starbucks to produce chilled coffee “Starbucks Frappuccino Coffee” in China. Zhejiang Feijian Industry & Trade Co, Ltd. is the original equipment manufacturer of Starbucks cups and drinking bottles.
There are countless industrial clusters in China, such as textiles in Jiangsu and Zhejiang provinces, metal goods or household appliances in Guangzhou province, the tobacco industry in Yunnan province, the coal industry in Shanxi province, and the automotive industry in Changchun of Jilin province. Another example is Zhongguancun in Beijing: It is a well-known center for science and technology and is also referred to as the Chinese “Silicon Valley”.

Government policy
Local government tax policies, regulatory approvals, and subsidies are factors that have a significant impact on a company’s location. Each Chinese provincial and municipal government has its own policies to promote foreign investment.
The way government subsidy policy works is that the local government provides subsidies to companies or investment projects in a particular industry to support that industry. For example, foreign companies receive certain tax benefits and special economic zones are established.
Advantages for foreign companies
China’s current preferential policies for foreign enterprises include VAT rebates (for domestic equipment purchased as part of the total investment amount), corporate income tax exemptions, or local income tax exemptions (only in some provinces and municipalities). In addition, some of the equipment and accessories for manufacturing products listed in the “Guojia Gaoxinjishu chanpinmulu (National High-tech Product Catalog)” are exempt from customs duties and VAT on import compounds. In addition, local governments sometimes offer special incentives for the establishment of certain enterprises.
Example: Tesla
For example, Tesla planned to set up in Jinqiao, Pudong, Shanghai in 2014. The goal here was to retain 100% control of the company. However, regulations at the time stipulated that foreign automotive companies must enter into joint ventures with local companies in order to locate production in China. In addition, it was stipulated that the Chinese party’s shareholding must not be less than 50%. The Chinese side then changed the requirements for electric vehicles in terms of the share ratio and the number of foreign joint ventures, which gave Tesla the opportunity to build a factory and operate a company that was 100% owned.
We support you in the choice of location
As a consulting firm operating in Europe for many years, we not only have a comprehensive understanding of the requirements and cultural practices of European companies, but also maintain close relationships with local Chinese governments, law firms, and other partners in China. As a result, we benefit from in-depth expertise and have access to a wide range of resources in the Chinese market.
At the same time, market research and data collection provide us with an accurate understanding of the labor market situation, industrial environment, and government policies in different regions of China. By matching these insights with industrial and corporate development plans, we obtain reference data and information that enable wise location decisions in China for greenfield investment projects.
